One of the biggest misconceptions about Waldorf education is that children can’t read and that Waldorf schools are anti-books.
In this week’s Sunday with Sarah , I try to dispel some of the myths and describe how reading is approached in Waldorf education.
I’m sure this topic will raise lots of questions, so please a comment below, and I will do my best to answer them all!
And if you want to be sure to catch all future videos, be sure to visit my Sunday with Sarah YouTube channel and SUBSCRIBE!
Warmly,

TRANSCRIPTION:
Today I’d like to dispel one of the biggest myths you may have heard about Waldorf education: that Waldorf kids can’t read. I’m here to tell you that is not true and to share with you some information about how reading is approached in Waldorf education.
Now, it’s true that Waldorf kindergartens and nurseries don’t formally teach reading, writing, and other academic subjects, but that doesn’t mean that the children aren’t gaining valuable development in those areas. In the early years, they’re developing so many pre-reading skills and language skills. Children in a Waldorf preschool environment—nursery or kindergarten—are hearing verses, they’re learning songs, they’re hearing stories and fairy tales. They’re hearing rich language and they’re hearing it repeated over and over. They might hear the same story every day for a week or two weeks or repeating a circle play with the same songs and verses until they really memorize them and learn them by heart.
They’re building mature vocabularies. If you meet a Waldorf kindergarten student, who might not be reading any words yet, you may notice that they have a very advanced vocabulary and spoken language skills.
One of the reasons Waldorf schools don’t push reading at a young age is that children’s brains are all wired differently and some children are predisposed to read early while others are not. Other children might be developing their physical skills first, and the decoding ability necessary to read will come later. Most children under the age of seven will be more advanced in some developmental areas than others.
Some children can get really frustrated when reading is introduced too early, before they’re ready. It can turn them off to reading for a lifetime, convincing them that reading is a chore and not inherently rewarding or fun. In Waldorf we choose to allow these skills to develop naturally at the individual child’s own pace. It’s similar to walking: kids learn how to do it on their own, at different ages, without us having to teach them how!
I always give the example of my two children. My older son, Harper, didn’t start to read fluently until the middle of 3rd grade. My younger son, William, taught himself in kindergarten. Nobody taught him, he just started reading one day. I, like a lot of parents, was really worried when their cousins were their age and reading way ahead of them, but both boys grew into very voracious readers with excellent literary skills. When it happens, it happens.
Around the age of seven, all those different developmental areas should be more or less caught up. Rudolf Steiner, the founder of Waldorf education, believed around seven, or the year the child is turning seven, is the ideal time to start first grade and academic learning.
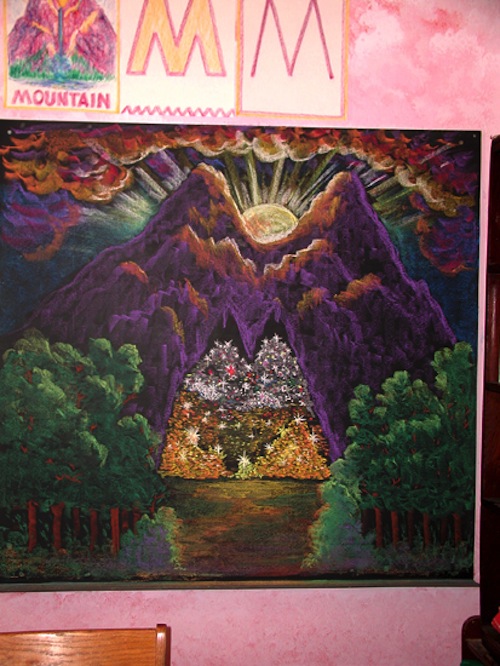
When they do get to first grade, letters are introduced in a very imaginative and living way through stories and art. For example, the letter “M” might be introduced as a drawing of a Mountain in the shape of the letter.
By third grade, most children in a Waldorf school should be reading competently. Some children do develop learning disabilities, such as dyslexia, so when they do get to grade school it’s important to keep an eye on them and to be in touch with a child’s teacher. If by third grade they’re still struggling, you may want to consult with a learning or reading specialist for analysis because the earlier a problem like dyslexia is diagnosed the more can be done to help the child.
I can assure you that Waldorf schools are not anti-reading and they’re not anti-books. Being concerned that your child is falling behind can be a natural reaction, but I’m here to tell you to relax and let it happen when it happens.
As always, your comments and questions are always welcome! Please leave them below and I will do my best to respond.